

It’s been another year of transformational research at Lawson Health Research Institute. Our teams have published groundbreaking findings and launched new studies that will have a profound impact on patient care.
The following are 12 highlights of research and innovation from across London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC) and St. Joseph’s Health Care London (St. Joseph’s). From trialing new cancer treatments to advancing understanding of mental health, our research teams have achieved a number of important milestones.

Lawson researchers continued to advance understanding of COVID-19 this past year. In one study, researchers found that unique patterns in blood plasma proteins of patients with suspected long COVID could act as a drug target to improve patient outcomes. Read more.
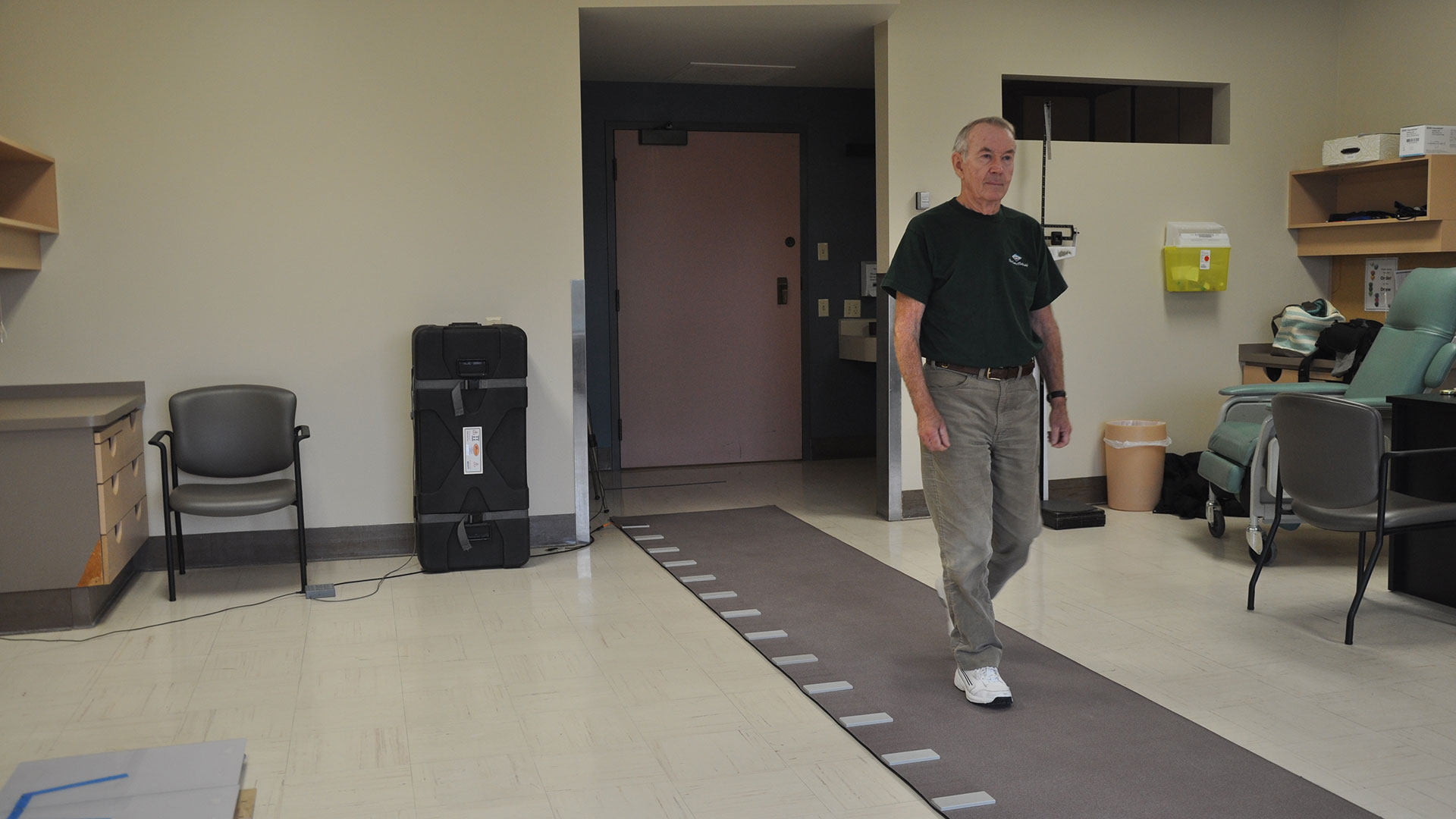

A study from Lawson and Western University found that a combination of computerized cognitive training and aerobic-resistance exercises can improve functions like memory, attention, recognition and orientation in older adults with mild cognitive impairment. The results suggest a new way to address declining mental sharpness in older adults. Read more.
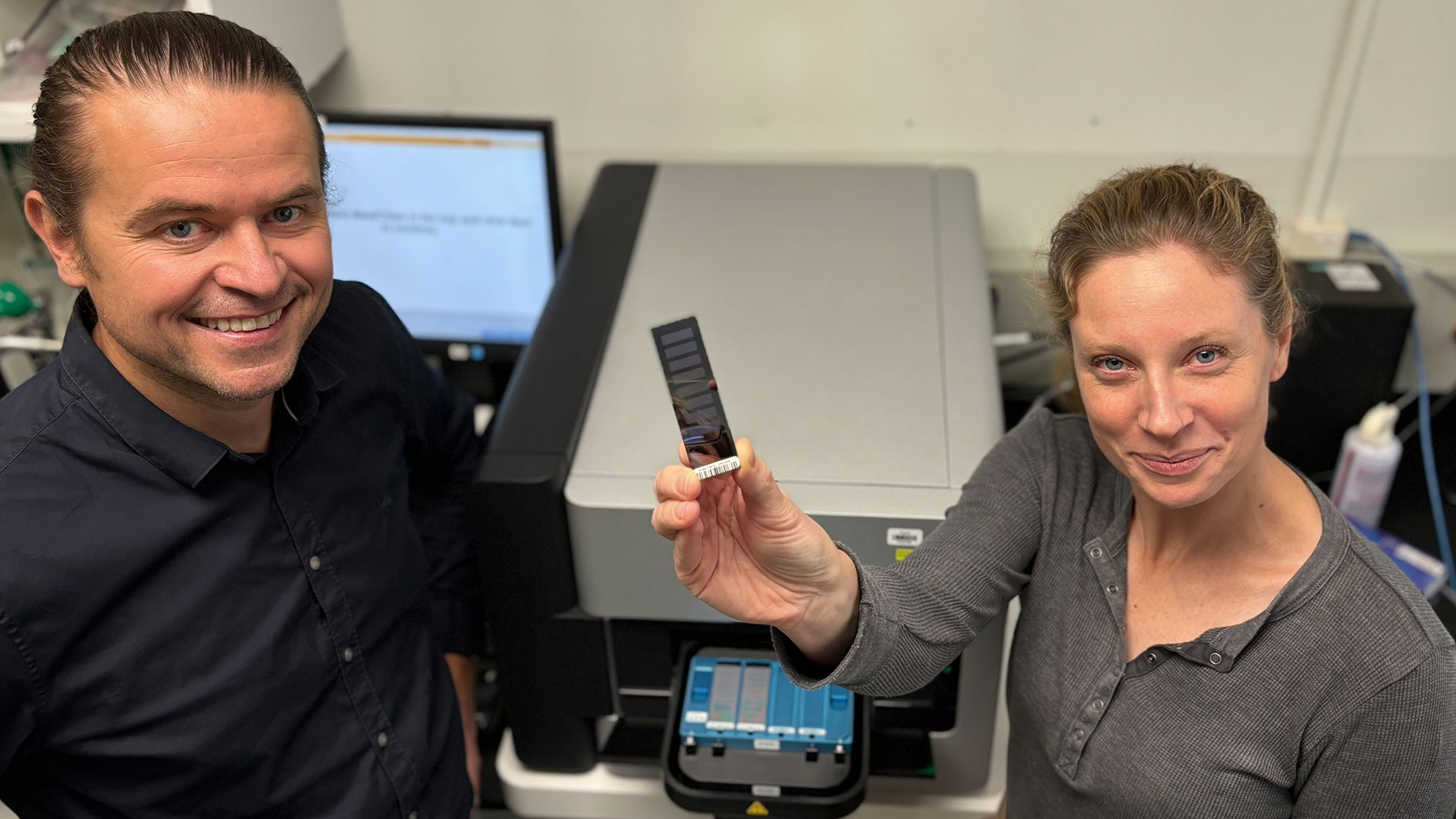

Technology to diagnose rare genetic disorders developed by researchers at Lawson and LHSC will be going global thanks to $7.55 million in funding from Genome Canada grant and Illumina Inc. The new artificial intelligence-led technology could allow rare diseases to be diagnosed with a simple blood test. Read more.
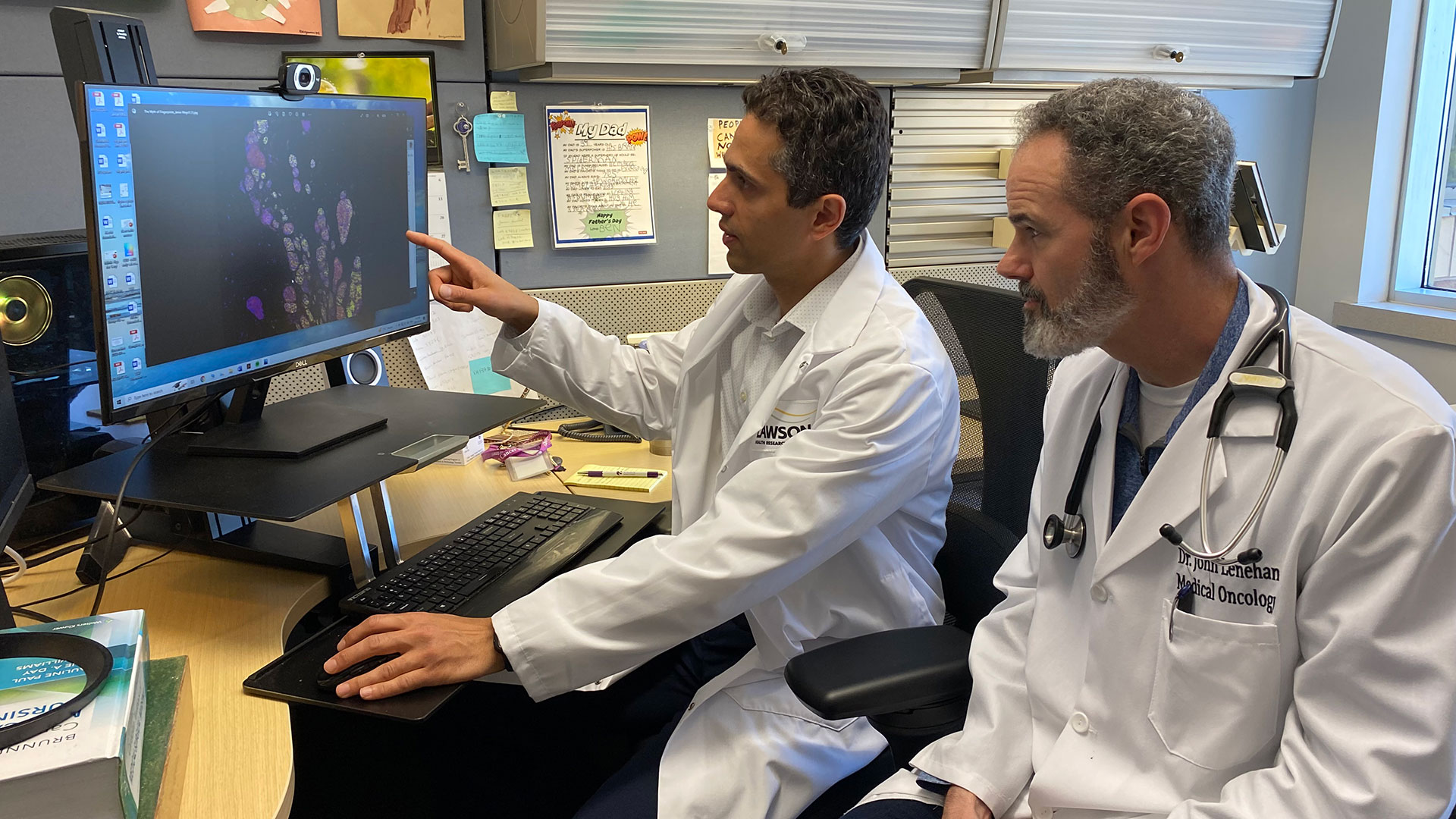

Fecal microbiota transplants (FMT) from healthy donors are safe and could improve response to immunotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma, according to results from a world-first multi-centre clinical trial led by Lawson researchers. Read more.

A team of Lawson researchers found that the use of ‘smart home’ technology like touch screen devices, activity trackers, weigh scales and medication dispensers may lead to better outcomes for those living with both mental health and physical disorders. The study found that participants using the technology started logging more exercise, making healthier food choices and not missing medication doses. Read more.
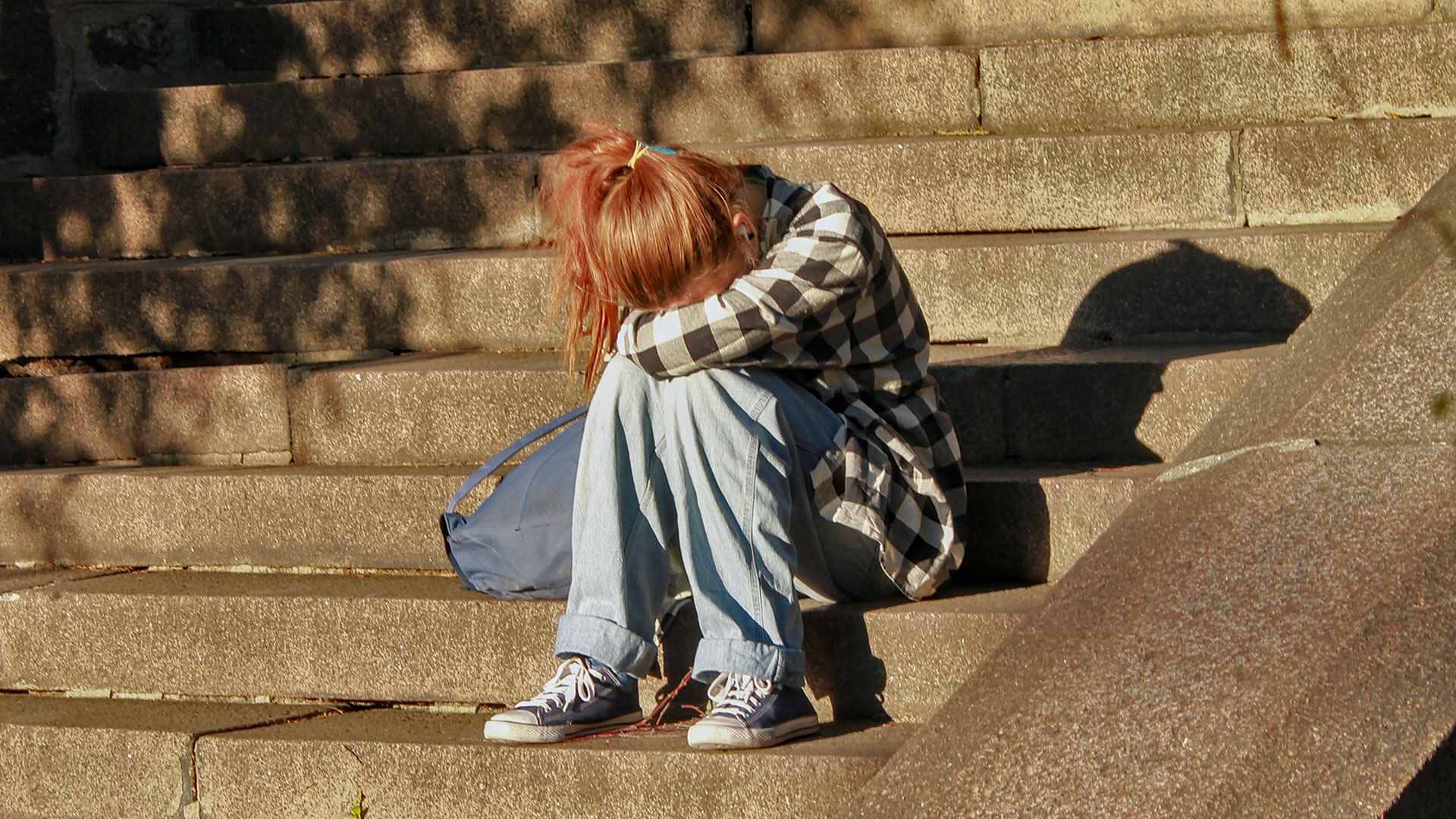

A national study with Lawson researchers found that during the first two years of the COVID-19 pandemic, adolescent emergency department (ED) visits and hospitalizations for suicidal thoughts, self-harm and self-poisoning increased across Canada, with the greatest increase occurring among adolescent girls. Read more.
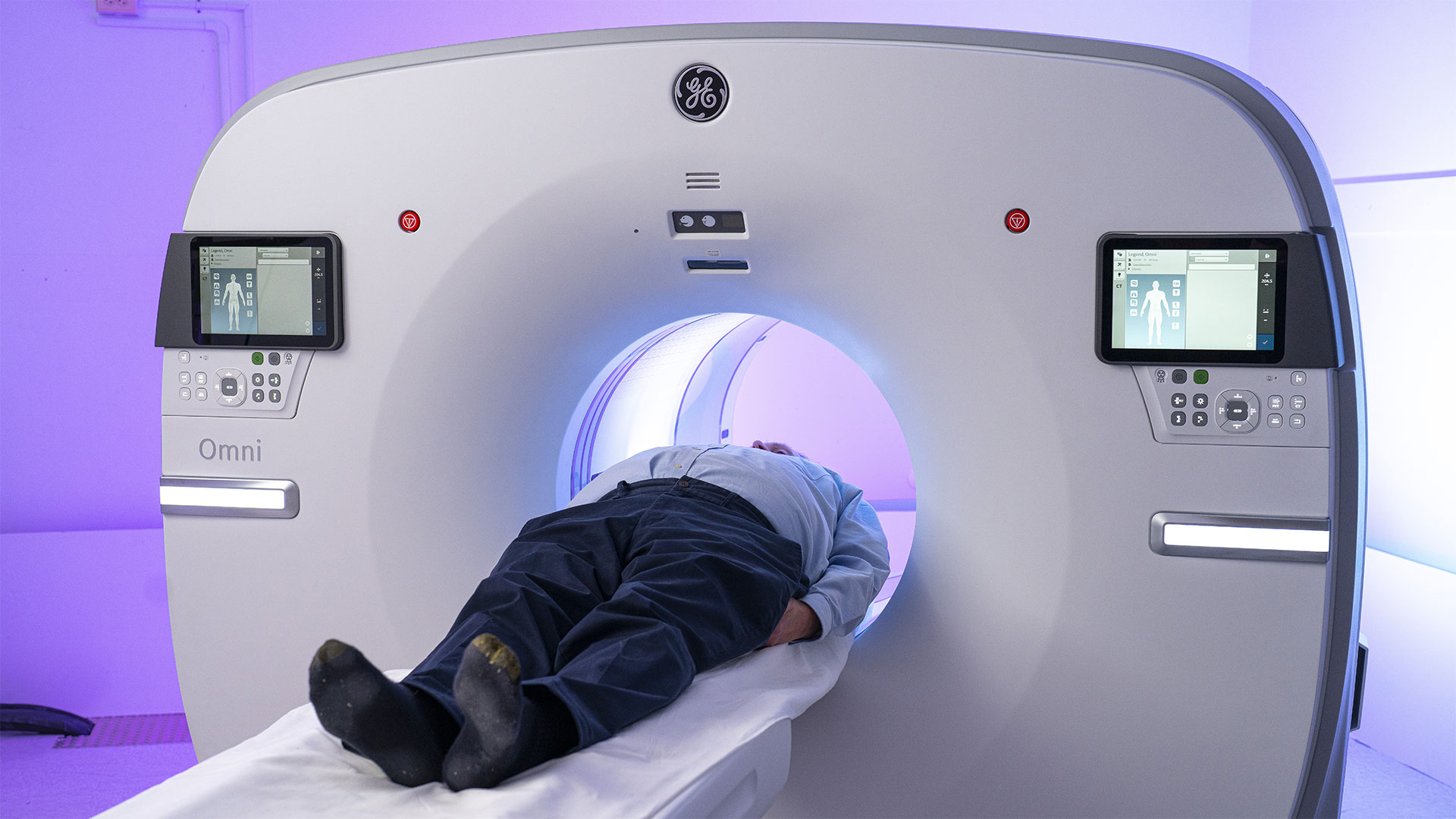
A partnership between Lawson, St. Joseph’s Health Care London and GE HealthCare will create Canada’s first centre of excellence in molecular imaging and theranostics at St. Joseph’s. The centre will focus on using precision diagnostic imaging and targeted therapy to advance personalized treatment of cancer and other diseases. Read more.
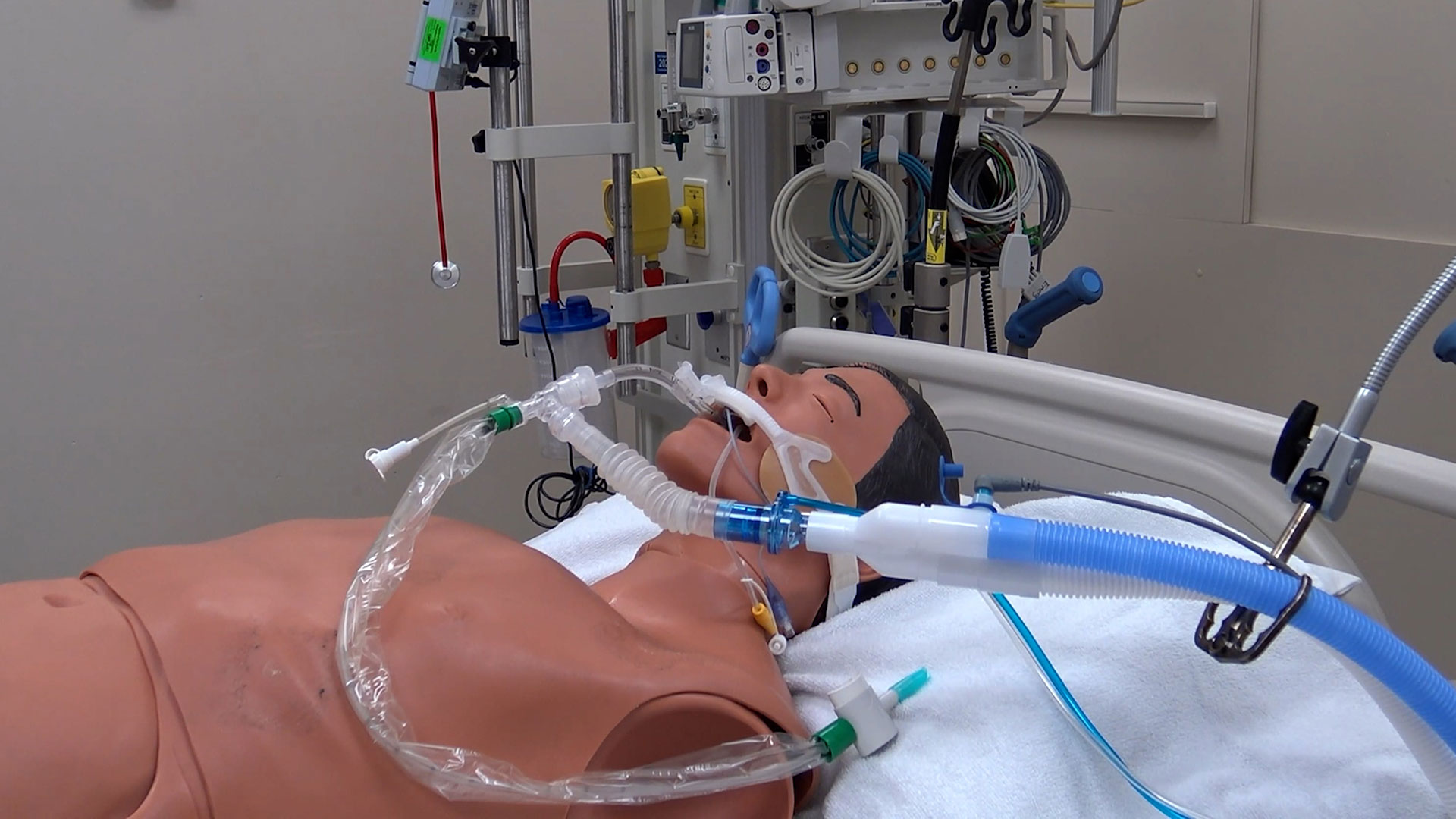
Intravenous sedatives are normally used to sedate critically ill children. However, they can contribute to a complication called delirium, which includes symptoms of confusion, disorientation, agitation, excessive drowsiness and poor attention. To improve outcomes, scientists at Children’s Health Research Institute (a program of Lawson), Sunnybrook Research Institute and The Hospital for Sick Children (SickKids) are collaborating on a pilot study to understand whether inhaled sedation could be a better alternative to keep critically ill children sedated and comfortable. Read more.
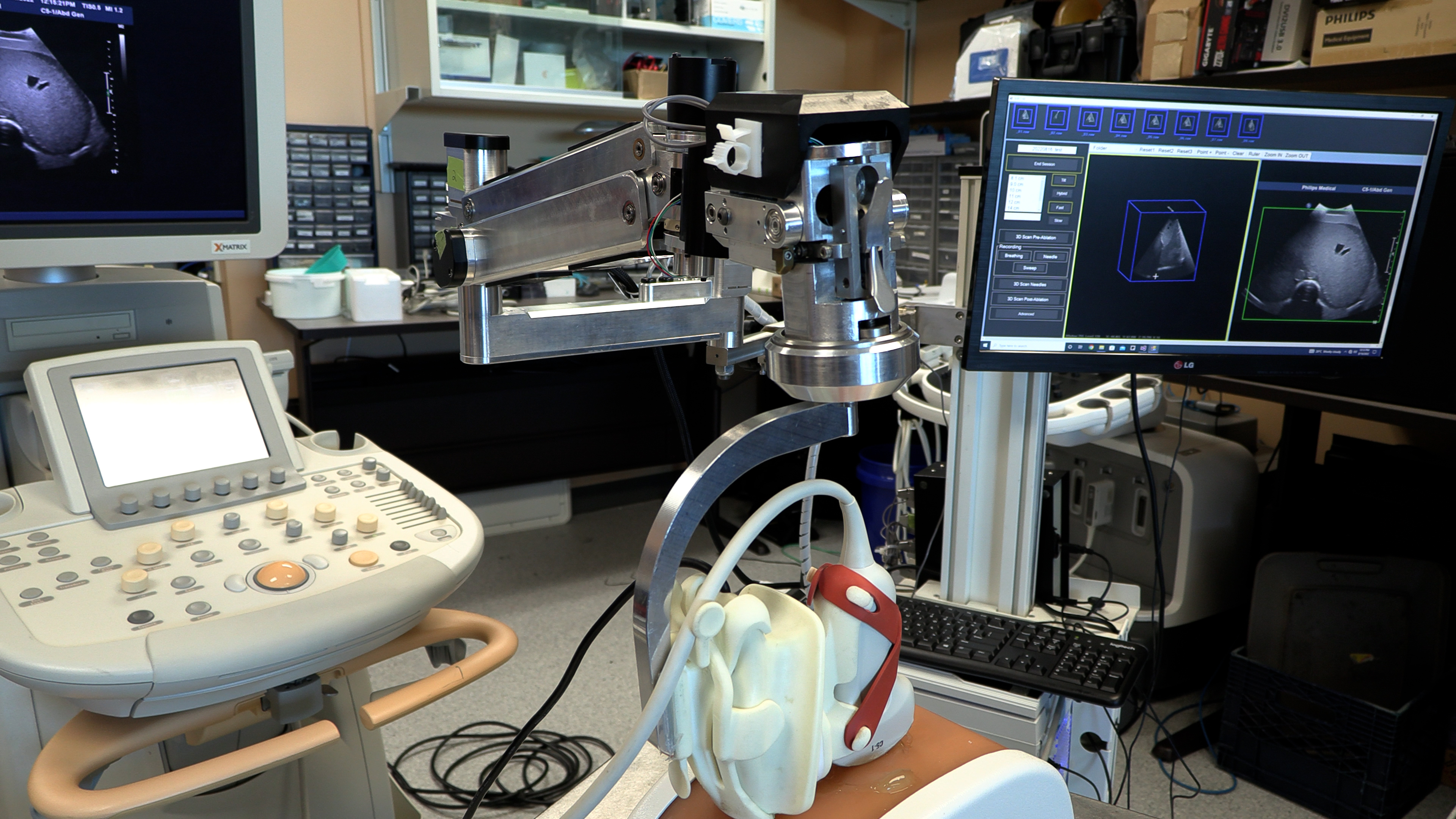
A technique that turns a normal ultrasound into a 3D image is showing promise in making thermal ablation for liver cancer treatment more accurate in a study from Lawson and Western University. Thermal ablation – using heat to destroy a cancerous tumour – can have fewer complications and a shorter recovery time than surgery. Read more.

Functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) is used to detect changes in brain oxygen levels using light, but more recently it has also been used to develop brain-computer interfaces – allowing patients with brain injuries to control a device with their thoughts. Researchers at Lawson launched a new study to assess whether fNIRS can be used to improve patient outcomes during stroke rehabilitation. Read more.

A preclinical study found that a specific type of inflammation may be linked to an increased risk of colorectal cancer. Previously, the degree of inflammation caused by illnesses like colitis, Crohn’s disease and other forms of inflammatory bowel disease were shown to be an important indicator of the development of colorectal cancer. However, this new study found the type of inflammation, rather than the severity and duration, may be more important in determining cancer risk. Read more.
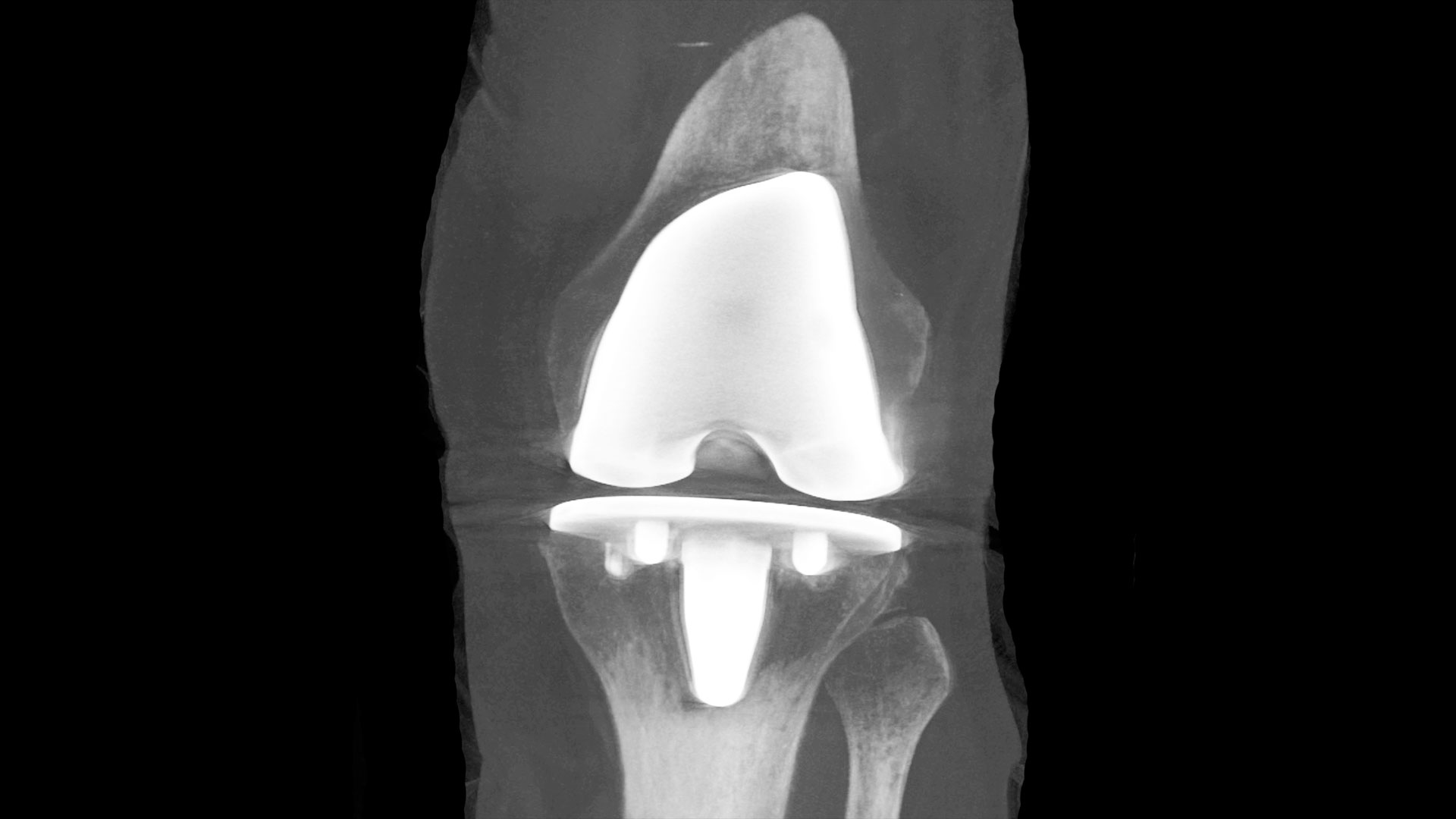
Lawson researchers launched a study to assess whether daily probiotics can improve outcomes in patients undergoing a total knee replacement surgery. Of the more than 70,000 knee replacement surgeries in Canada each year, nearly 10 per cent of patients experience complications. With patients who are considered healthy likely to have better outcomes, the research team is interested in improving the gut microbiome as a way to support patients’ overall health. Read more.
Communications Consultant & External Relations
Lawson Health Research Institute
T: 519-685-8500 ext. ext. 64059
C: 226-919-4748
@email