
LONDON, ON – A new system that turns ultrasounds into a 3D image could make treatment of liver cancer using thermal ablation more accurate, a new simulated study from Lawson Health Research Institute and Western University has found.
Liver cancer is the fourth leading cause of cancer death globally. While surgery is one treatment option, thermal ablation, using heat to destroy the cancerous tumour, can have fewer complications and a shorter recovery time. It can also be used for patients who are not surgical candidates.
Thermal ablation requires precise needle placement to treat the cancer without damaging the vital organs and blood vessels around it.
“It's very important that we get the needle right in the centre of the tumour,” says Dr. Derek Cool, Associate Scientist at Lawson, Assistant Professor at Western University’s Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry and Interventional Radiologist at London Health Sciences Centre (LHSC). “If the treatment area doesn't fully cover the tumour, patients are left with a small amount of residual cancer, risking recurrence and the need for additional treatment.”
Ultrasound or CT (computerized tomography) imaging is normally used to guide needle placement, but both are limited. Ultrasound is widely available and can be done in real-time, but only delivers a 2D image. While a CT scan provides a 3D image, it isn’t in real-time and can be a lengthy process.
“We developed a new 3D ultrasound method that shows promise in analyzing whether the complete liver tumour will be ablated by the procedure,” explains Dr. Aaron Fenster, a Professor at Schulich and Scientist at Robarts Research Institute. “And we're now using the same system to guide the needle directly into the centre of the tumor.”
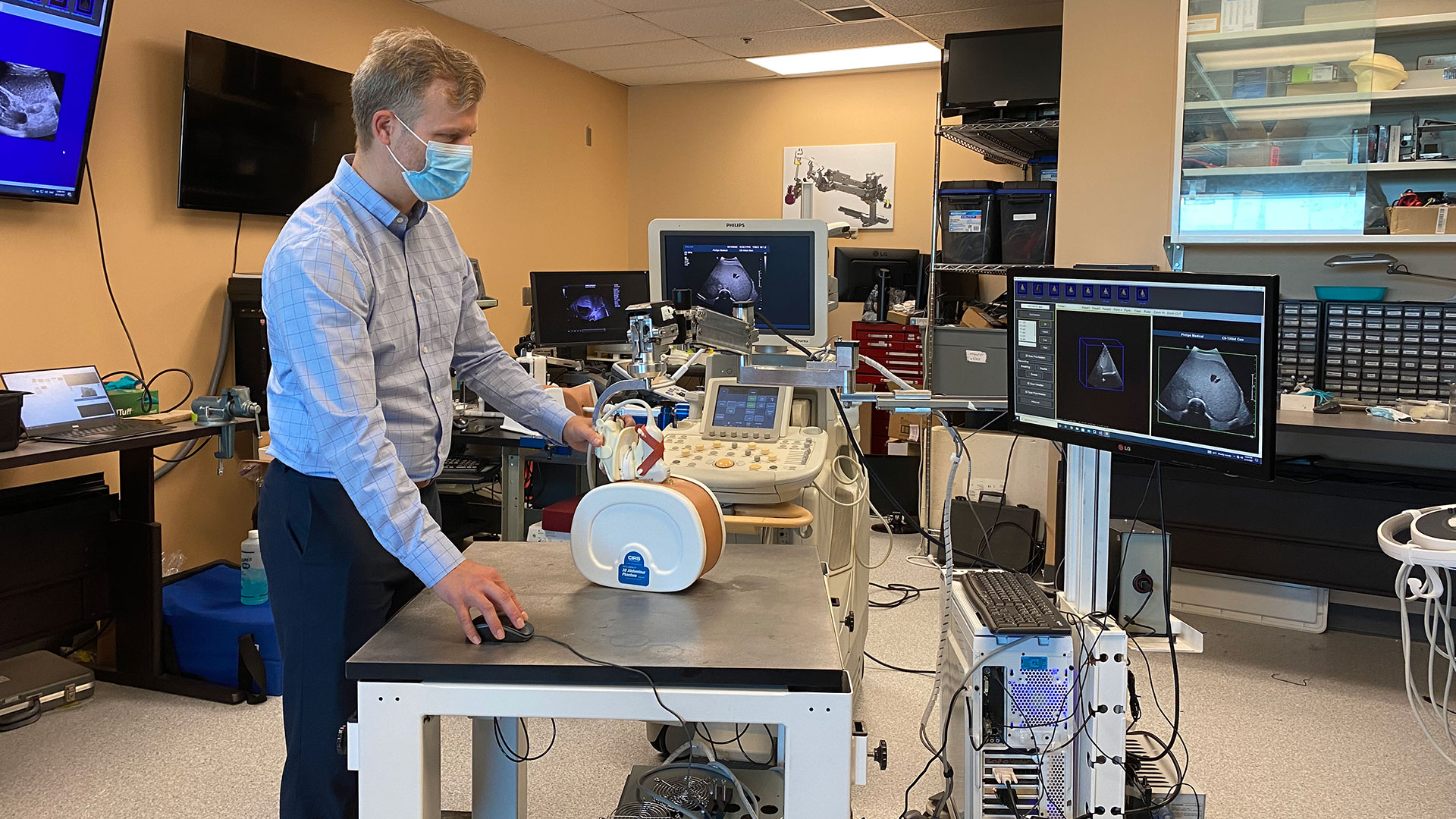
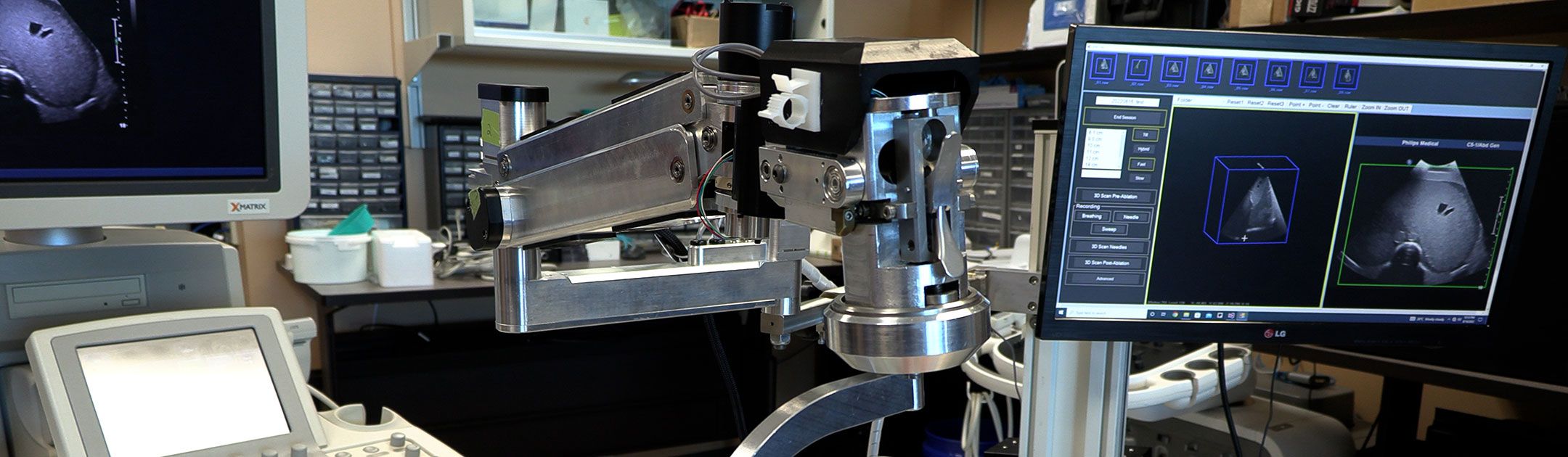
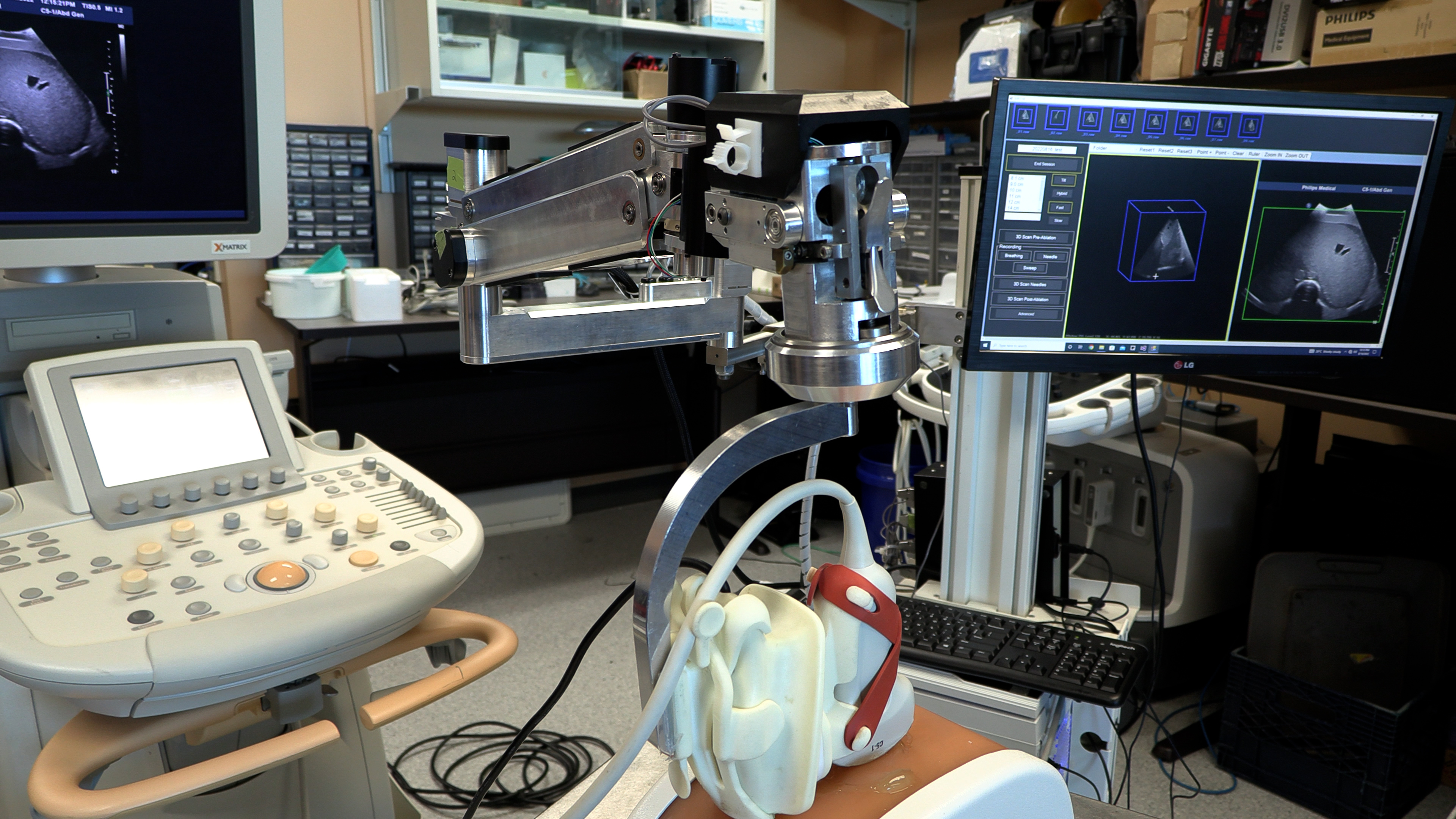
To create the 3D ultrasound images, a robotic cradle moves a standard ultrasound probe, collecting images and stacking them like puzzle pieces.
The simulated study, published in IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, used data from 14 patient cases at LHSC to analyze accuracy of the technology. It found that while 64.3 per cent of cases showed complete tumour coverage with standard imaging methods, the new system could result in complete coverage for 92.9 per cent of cases (13 of 14 cases). The researchers found that the remaining case could benefit from increasing the ablation time or intensity.

“Our next step is to move from simulation studies to a clinical trial,” says Dr. Cool.
If proven effective, the robotic ultrasound system’s portability could potentially allow for more widespread use of 3D ultrasound imaging, including in smaller health care centres. By eliminating the need for CT scans, it could also help to reduce imaging wait times.
“If a clinical trial shows the approach is more accurate and more precise than conventional techniques, there would be a direct impact on patient care,” says Dr. Fenster. “We hope to explore commercialization to license the technology and distribute it worldwide.”

Lawson Health Research Institute is one of Canada’s top hospital-based research institutes, tackling the most pressing challenges in health care. As the research institute of London Health Sciences Centre and St. Joseph’s Health Care London, our innovation happens where care is delivered. Lawson research teams are at the leading-edge of science with the goal of improving health and the delivery of care for patients. Working in partnership with Western University, our researchers are encouraged to pursue their curiosity, collaborate often and share their discoveries widely. Research conducted through Lawson makes a difference in the lives of patients, families and communities around the world. To learn more, visit www.lawsonresearch.ca.
Western delivers an academic experience second to none. Since 1878, The Western Experience has combined academic excellence with life-long opportunities for intellectual, social and cultural growth in order to better serve our communities. Our research excellence expands knowledge and drives discovery with real-world application. Western attracts individuals with a broad worldview, seeking to study, influence and lead in the international community.
The Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry at Western University is one of Canada’s preeminent medical and dental schools. Established in 1881, it was one of the founding schools of Western University and is known for being the birthplace of family medicine in Canada. For more than 130 years, the School has demonstrated a commitment to academic excellence and a passion for scientific discovery.
Communications Consultant & External Relations
Lawson Health Research Institute
T: 519-685-8500 ext. ext. 64059
C: 226-919-4748
@email